Pull Requests
Works with:
GitHubThis dashboard provides insights into Pull Request (PR) activity within a software repository. It includes four distinct charts, each designed to highlight different aspects of PR management and team dynamics.
Each chart in the dashboard is interactive and supports filtering by author, labels, and date range, allowing you to drill down into the data that matters most for your team. This enables you to monitor team flow and identify bottlenecks.
Summary PRs data
Show a summary of the PRs fetched from the repository, including total PRs, average open time, and other key metrics.
Not available yet.
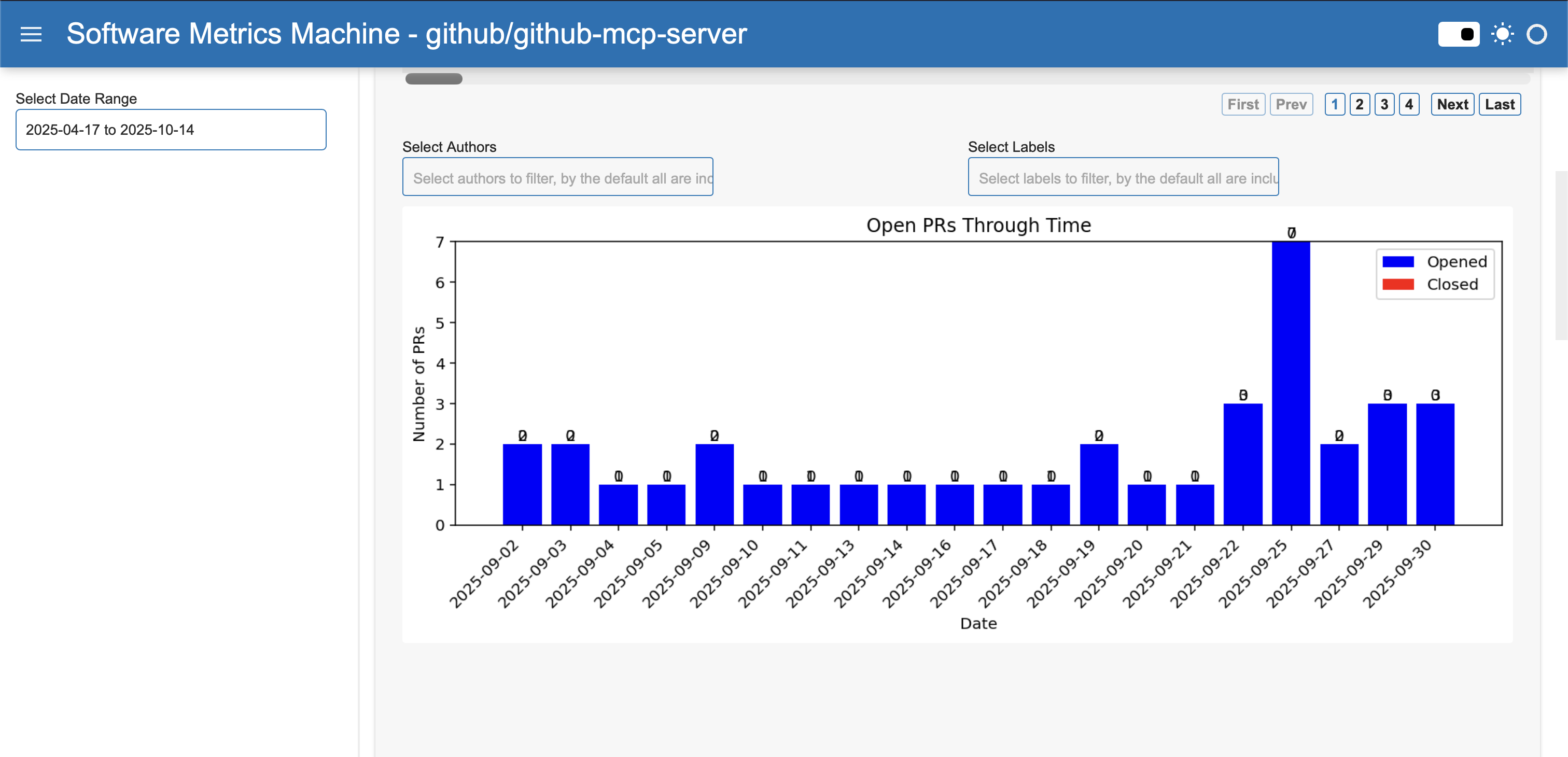
Open PRs Through Time
Shows the volume of PRs opened and closed each day. This helps you spot bottlenecks, busy periods, or trends in your team's workflow.
If you notice a spike in opened PRs but few closed ones, it may indicate the start of a new sprint or a backlog forming. For example, if September 25th shows many opened PRs but none closed, it could signal a need to focus on reviews.
How It Computes and Filters
- Aggregates PR events by day.
- Filters by date range (start/end date) - the date used in the prs are the created_at.
- Data is processed to count opened and closed PRs per day.
- You can filter the chart to focus on specific periods, such as a sprint or release window.
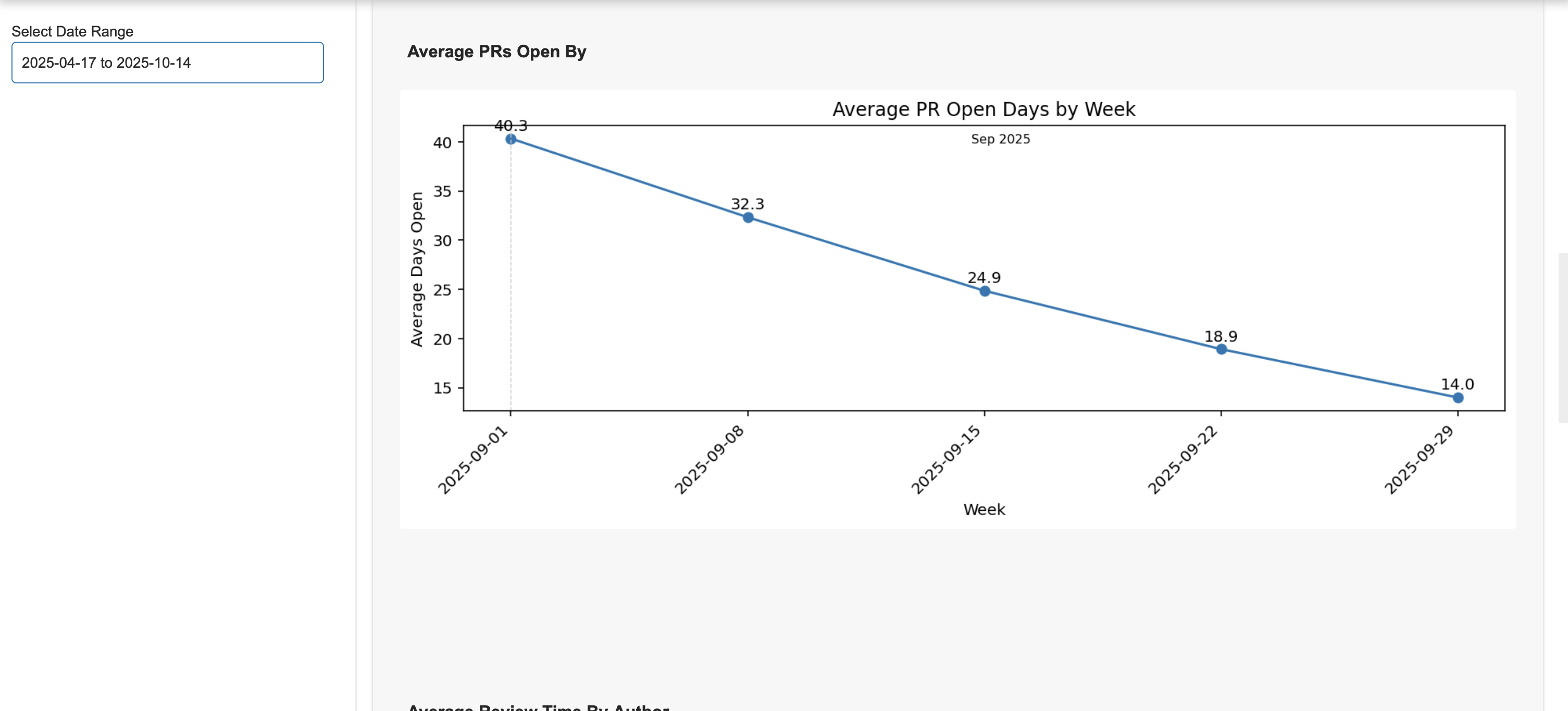
Average PR Open
Tracks how long PRs stay open before merging. It uses weekly or monthly aggregation to show trends in review speed.
How It Computes and Filters
- Calculates the average number of days PRs are open, grouped by week or month.
- Supports filters for author, labels (e.g., bug, enhancement), and date range.
- Aggregation smooths out daily fluctuations, showing long-term trends.
Average Review Time By Author
Plot the average time taken from the team to review a PR open by an author and merge it. The result is shown in average by days.
Example Usage
If one author consistently has longer open times, it may indicate complex PRs or a need for more review support. For example, if Alice's PRs average 7 days open while others average 2, you can investigate further.
How It Computes and Filters
- Computes average open time for each author.
- Filters by top N authors, labels, and date range.
- Data is processed to exclude bots or focus on specific contributors.
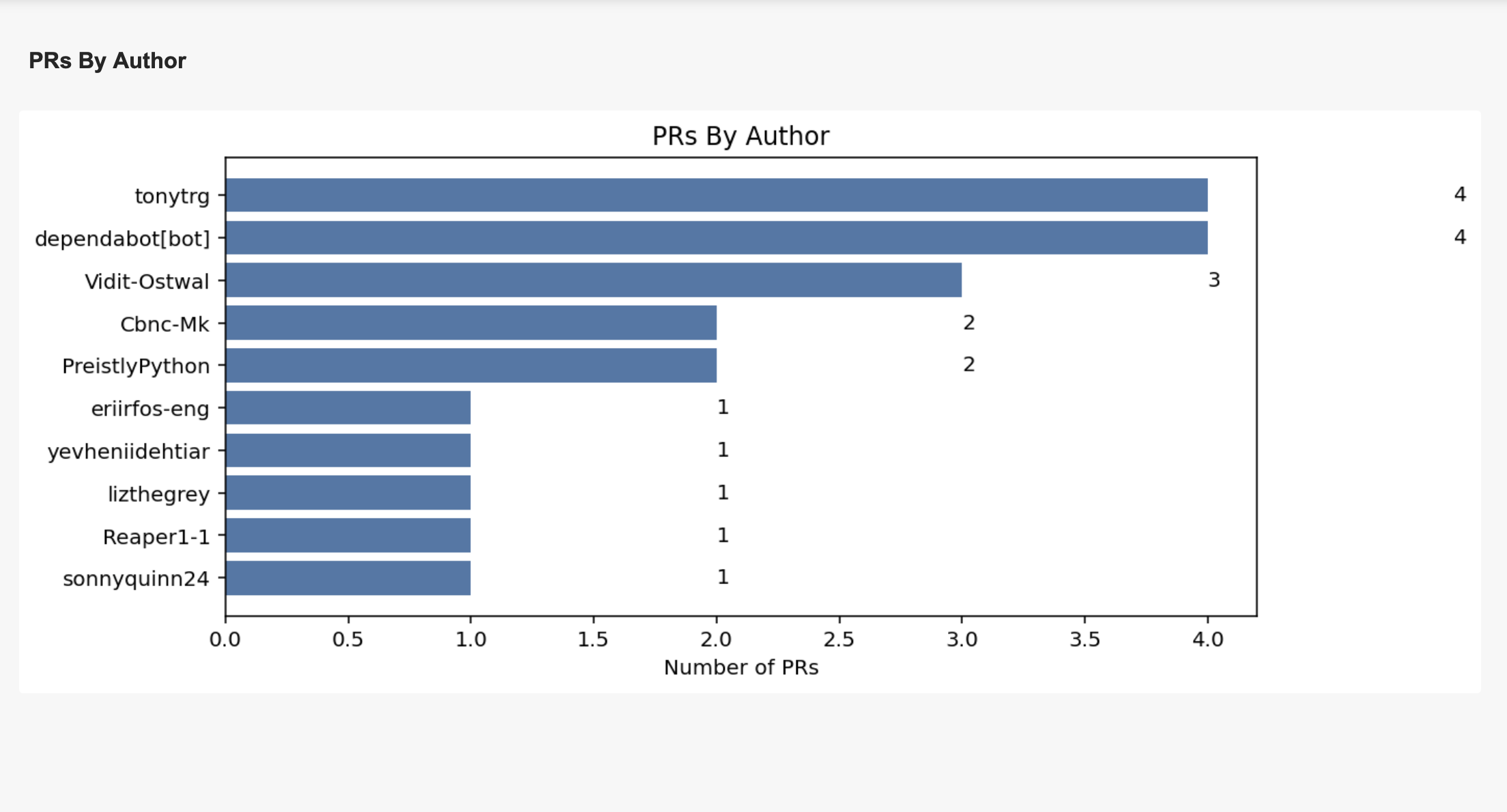
PRs By Author
Example Usage
If one developer is opening most PRs, you may want to redistribute tasks or recognize their effort. For example, if Bob opened 30 PRs in a month, he’s a key contributor.
How It Computes and Filters
- Counts PRs opened by each author.
- Filters by top N authors, labels, and date range.
- Includes bots (e.g., dependabot) to show the impact of automation.
Average Comments per PR
Plot the average number of comments a PR receives before it is merged, aggregated by week or month.